GST Login:
One of India’s most notable indirect tax reforms is the Goods and Services Tax (GST). It completely altered the national taxation system when it went into effect on July 1, 2017. However, how does GST and GST Login work, and what is it anyway? Allow me to explain it in layman’s words.
What is GST?
The Goods and Services Tax (GST) is essentially just one all-encompassing indirect tax on product and service supply. Excise duty, service tax, VAT (Value Added Tax), and a tangled web of other federal and state taxes were supplanted by it. The fundamental objective was to establish a uniform national tax structure that would facilitate easier trade and commerce.
Get this picture: you’re going to buy something. Before GST, there may have been other hidden taxes included in the amount you paid. The Goods and Services Tax (GST) unifies most of these levies into a single, transparent rate.
GST Status & Login:
In India, the Goods and Services Tax (GST) is a tax on purchasing and selling products and services. The new system, which went into effect on July 1, 2017, replaced several indirect taxes with one that was easier to understand and created one big national market. GST has varying tax rates for different types of goods and services, such as 0%, 5%, 12%, 18%, and 28%. Businesses are mostly responsible for paying GST, but it also affects the costs that consumers pay. One of the best things about the system is that businesses may frequently get credit for the taxes they’ve already paid on their purchases, which lowers the amount of tax they have to pay overall. Businesses must register under GST and file returns regularly to be in compliance. When transferring products worth more than a specific amount, you need an e-way bill to do so. There is a simpler way for small businesses to pay their taxes. Also, items are given specific numbers called Harmonized System of Nomenclature (HSN) codes to figure out what the tax rate is. GST regulations and rates aren’t set in stone; they can vary from time to time to meet the demands of the market and changes in policy.
The Structure: CGST, SGST, and IGST:
India implements a dual GST system:
Key Benefits of GST:
Eliminating the Cascading Effect:
GST addresses the “tax on tax” issue, facilitating input tax credit and lowering overall tax expenses.
Streamlined Tax Framework:
Merges multiple taxes into a single entity, facilitating compliance.
Improved Inter-State Trade:
Promotes seamless trade across state lines with reduced checkpoints.
Increased Tax Base:
The tax base has expanded as a result of a greater number of registered businesses, leading to an increase in government revenue.
Enhanced Compliance:
Digital procedures for registration, returns, and payment simplify tax adherence.
GST Rates: Slabs and How They Work
The GST system comprises several tax slabs: 0%, 5%, 12%, 18%, and 28%. Basic necessities are subject to lower rates, whereas luxury or undesirable items incur higher rates. Certain items, such as gold, are subject to specific rates (e.g., 3%). The GST Council evaluates and modifies these rates as necessary.
Impact on Consumers and Businesses:
Consumers: In the long run, prices could decrease as cascading taxes are removed. The effect differs depending on the product or service.
Businesses are experiencing notable transformations in invoicing, accounting, and supply chains. Managing compliance and input tax credits is crucial.
Challenges and the Way Forward:
GST Login Process:
If you are a first-time user:
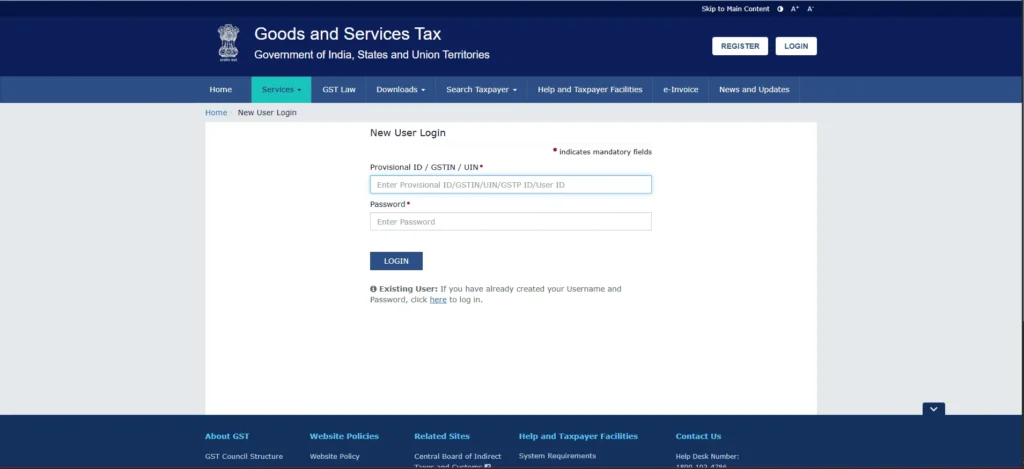
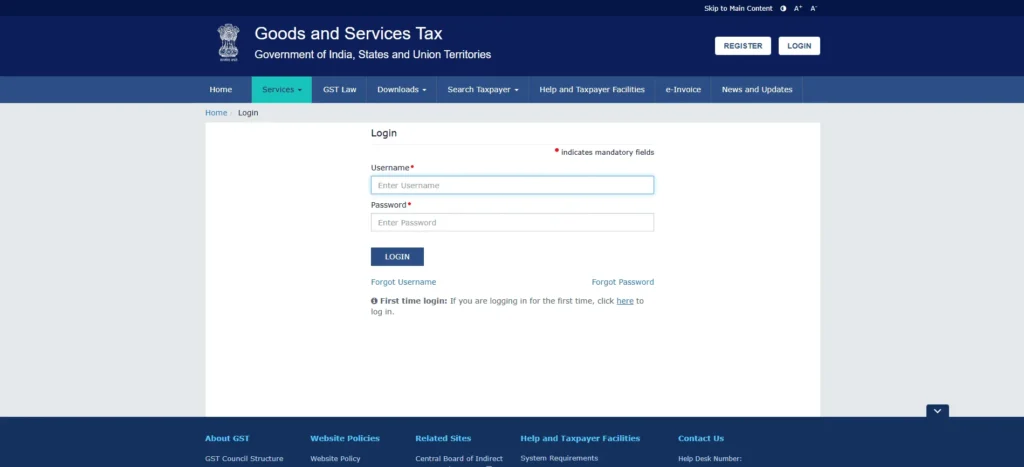
If you are an existing user:
GST Registration Process:
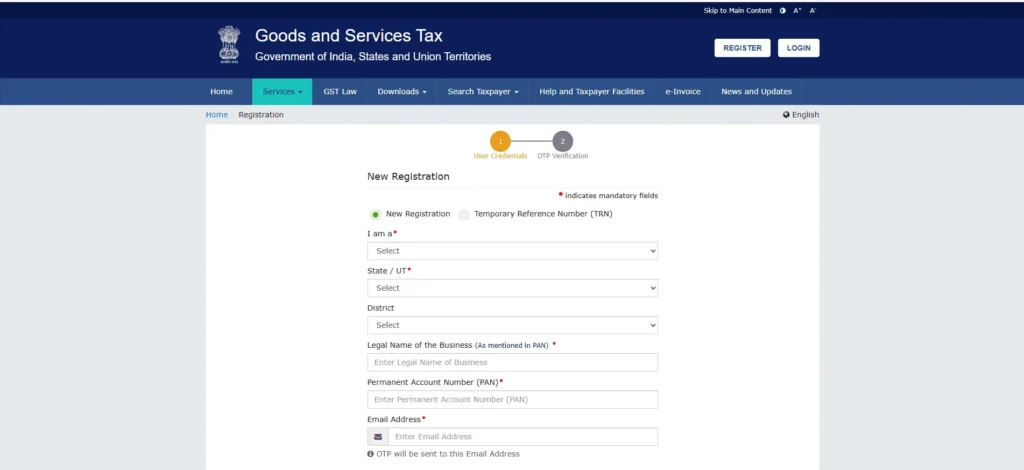
Section A – Fundamental Information:
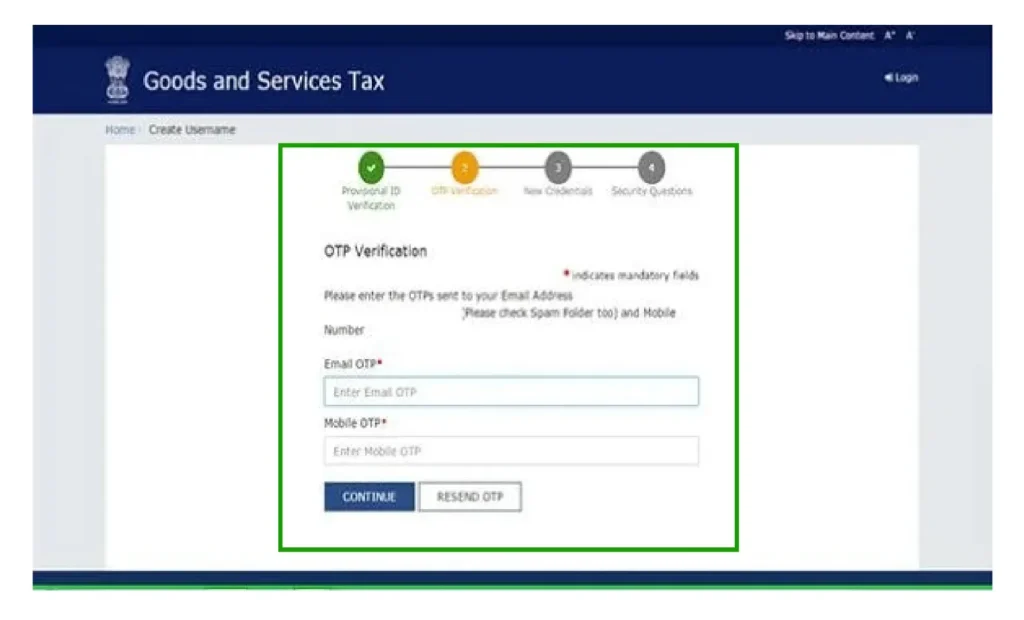
OTP Verification:
Please enter the OTPs that have been sent to your email and mobile, and then click on PROCEED.
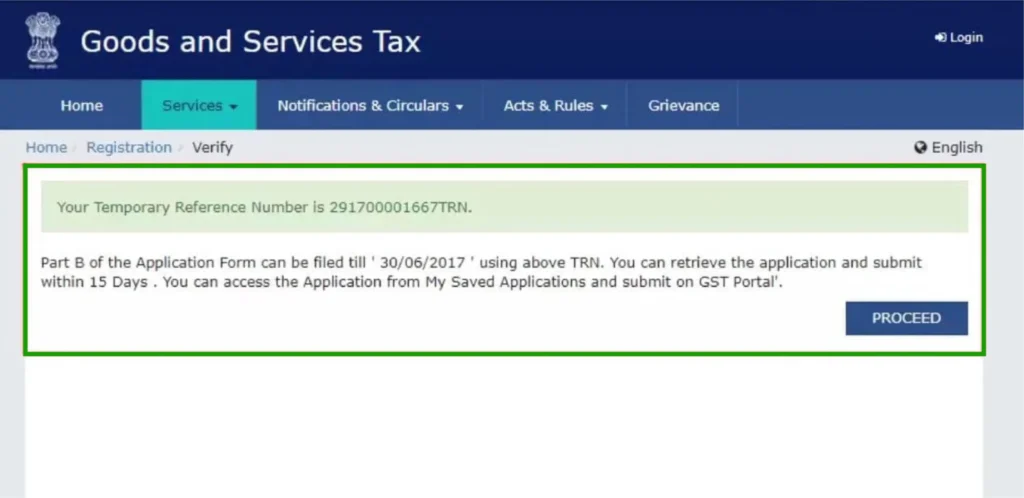
Temporary Reference Number (TRN):
Please be aware of the TRN that has been sent to your email and mobile device.
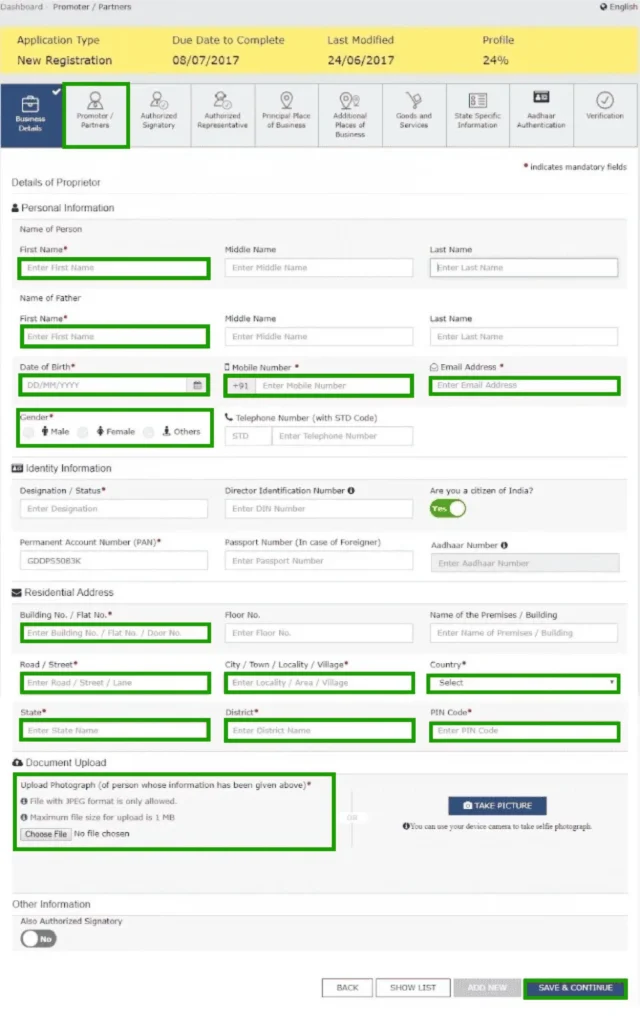
Part B – Detailed Information:

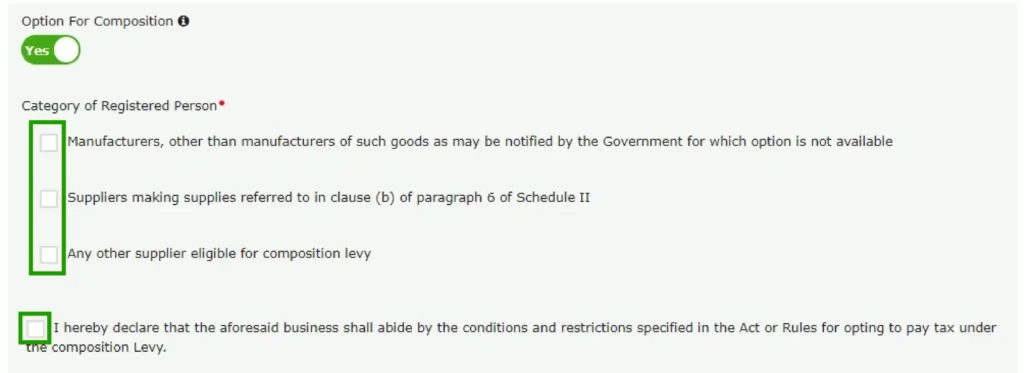
Please complete the sections of the application form as follows:
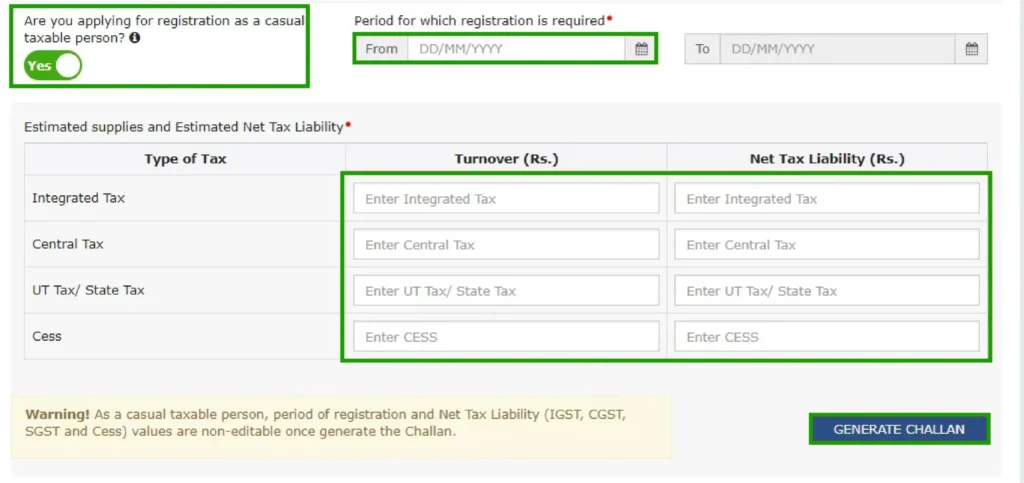
Please upload the necessary documents: PAN card, address proof, bank details, photographs, and so on.
Submit via DSC or EVC.
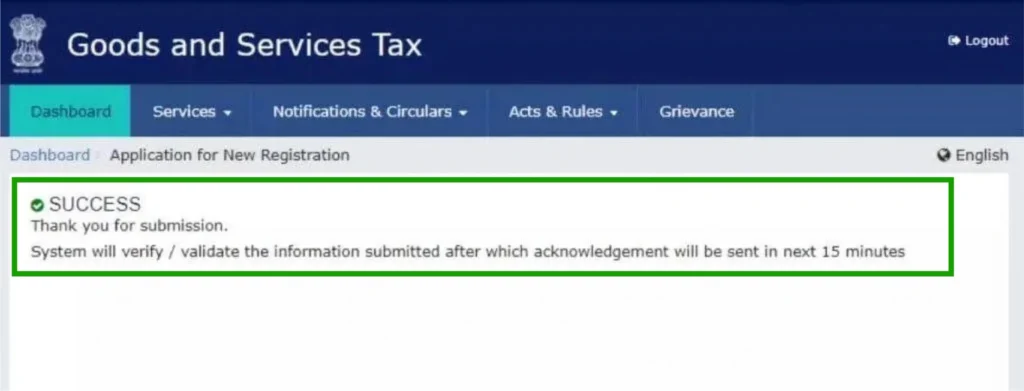
Your registered email and mobile will receive the ARN shortly.
The GST officer reviews your application and supporting documents for verification.
Once approved, you will be issued your GSTIN along with the Registration Certificate (Form GST REG-06).
Ensure that you have all necessary documents readily available before you begin. The requirements for documentation can differ depending on the type of business.
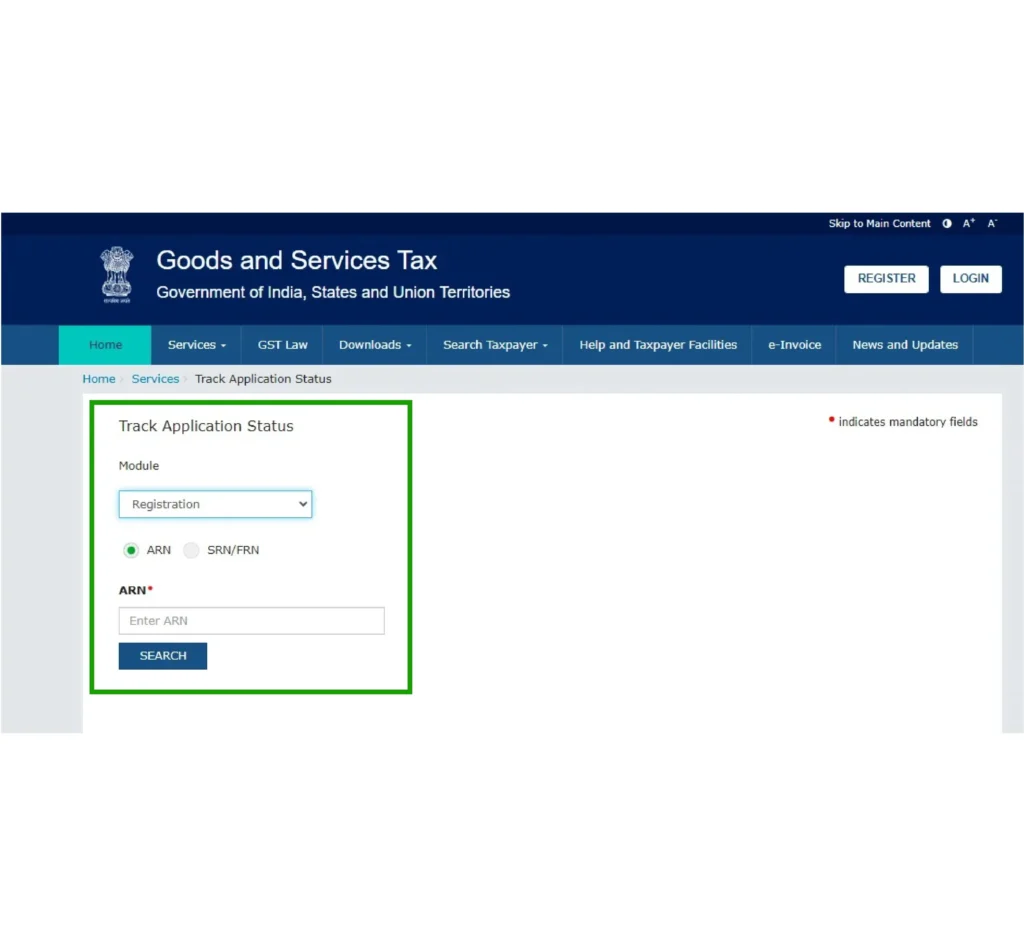
Checking Status After Login (Using ARN or Submission Period)
Possible Application Statuses:
It is advisable to monitor your status frequently and promptly address any requests for clarification to prevent any potential delays.
In Conclusion:
The Goods and Services Tax (GST) in India represents a pivotal tax reform that has profoundly altered the economic landscape. Despite facing initial challenges, the long-term advantages of establishing a unified market, streamlining taxation, and alleviating the tax burden are clear. As the system evolves and additional enhancements are implemented, GST will remain a crucial factor in India’s economic growth and development. Being aware of the most recent GST rules and regulations is essential for businesses and consumers alike to effectively navigate this changing system.
